Operating Principle of Pumps
Pumps play an important role in transporting various liquids, such as oil, cement, water, oil, fuel, or coolant. They also evacuate air from household containers, creating a vacuum. This is just a small part of their functions.
Pump Control: Necessity
A pump cannot operate without an electric motor, which is connected to a special device for regulating pressure or vacuum. The most effective method of control is the use of frequency converters, which provide the electric motor with the minimum necessary energy to maintain the set pressure. This can reduce energy consumption by more than 30%, which, in turn, can save over 80,000 hryvnias per year.
Pressure Regulation Principle
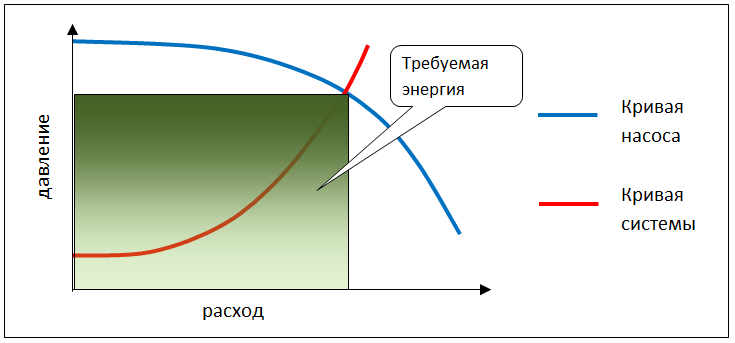
It is important to understand that the power of the installation should be selected for a specific system, taking into account the maximum level of consumption. Often, the system does not meet the needs, and a situation arises where the installation power is excessive.
In uncontrolled systems, even with the use of throttling, the pump can create excess pressure due to reduced flow, which leads to increased electricity costs.
Installing a frequency converter can correct the situation by adapting the pump curve according to system requirements by reducing the motor's RPM.
Need for Pump Regulation
Water consumption varies depending on the time of day and seasonality. Often, on holidays or weekends, when many people use water simultaneously, there is a sharp increase in consumption.
Addressing the issue of improving regulation efficiency may include:
- minimizing electrical energy costs and investments in equipment modernization;
- maximizing regulation results.
To achieve these goals, frequency-controlled drives (FCDs) are used, which pay off within a year to a year and a half. They can reduce energy consumption by up to 50%, thereby also eliminating problems with hydraulic shocks that can damage pipelines.
Choosing a Frequency Converter for Pumps
The choice of the type of frequency converter depends on the specifics of the task. For example, for controlling low-power pumps (0.2-2.2 kW), a single-phase converter is sufficient, such as Bosch series ConverterFe or Bosch series EFC3610, which do not require additional capacitors. Three-phase models, such as Bosch series ConverterFe, can operate up to 160 kW.