The Importance of Frequency Converters in Modern Automation Systems
 In modern production automation systems, frequency converters play an important role.
In modern production automation systems, frequency converters play an important role.
They are widely used in the fields of water supply, heating, compressor installations, as well as in ventilation and air conditioning systems. Frequency converters replace uncontrolled drives with asynchronous motors, which significantly simplifies mechanical systems, increases their reliability, and reduces operational costs. When connecting a frequency converter, the motor starts smoothly, which reduces the load on the motor itself and other mechanisms, contributing to extending their service life. One of the main advantages of frequency converters is their energy efficiency, which can reach 75% due to the reduction of motor power and the absence of losses during inrush currents.
Applications of Thyristor Frequency Converters
Thyristor frequency converters are increasingly used in regulated drives with direct current motors. They are capable of maintaining the required speed under conditions of variable load. However, it should be noted that such motors have a collector, which complicates their use in dusty or explosive environments.
To reduce the requirements for the operating environment, enhance reliability, and lower costs, regulated drives based on asynchronous motors are being used more frequently.
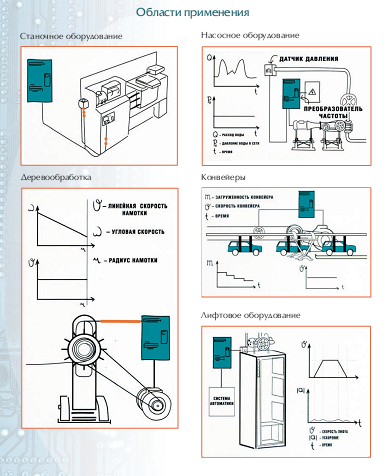
Areas of Application of Frequency Converters
Regulated electric drives that operate based on frequency converters are used in many areas:
- Water and Heating Supply Systems: Frequency converters in pumps allow for regulating water supply and maintaining the necessary pressure level, preventing hydraulic shocks. This reduces water consumption, lowers the risk of pipeline damage, and saves electrical and thermal energy.
- Production of Textile and Polymer Materials: In the processes of manufacturing paper, fiberglass, and during the winding of threads and films, it is necessary to accurately control several motors simultaneously to avoid breakages.
- Precise Positioning of Mechanisms: For solving precision positioning tasks, converters with vector control are used, which provide feedback and can operate with maximum torque at zero speeds.
