Digitalization of Industry: Industry 4.0 and the Industrial Internet Consortium
When considering the digitalization of industry, it is important to focus on two key areas: the concept of Industry 4.0 and the activities of the Industrial Internet Consortium (IIC). How do they interact and what are their main objectives?
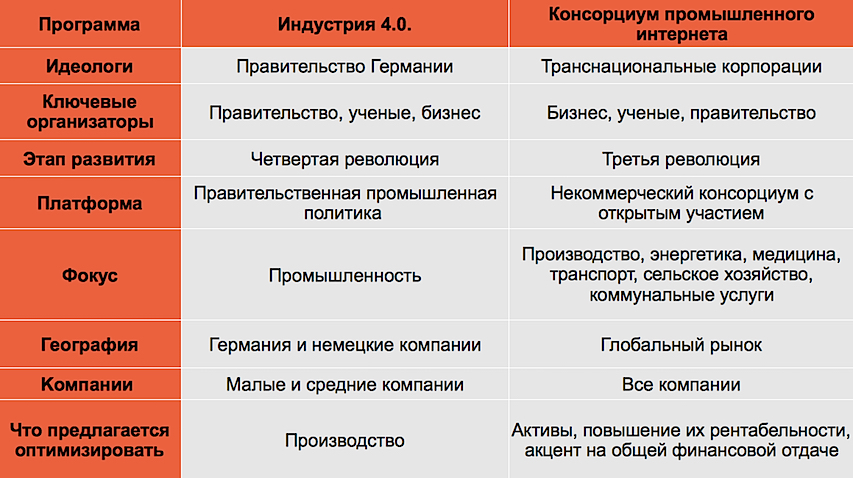
What is Industry 4.0?
Industry 4.0 is a future-oriented project that is part of the German federal government's high-tech strategy. The main goal of this project is to create innovative solutions for German industry in the era of the Internet. The key areas of focus include:
- Horizontal integration: improving the value-added processes through IT technological support.
- Vertical and full integration: integrating all engineering mechanisms into the value creation chain.
- Networked production systems: ensuring vertical integration in manufacturing processes.
In 2015, the Industry 4.0 platform was reorganized at the Hanover Fair, including companies such as Festo, SAP, Siemens, Telekom, as well as the Federation of German Industries (BDI). This platform unites the efforts of the private sector, academia, politics, and other areas to promote the development of Industry 4.0. One of its goals is to coordinate regional regulations to avoid mistakes made during the implementation of mobile telecommunications.
Industrial Internet Consortium (IIC)
The IIC was founded in March 2014 and brings together technology companies, research institutions, universities, and governmental organizations. For example, Siemens became a part of the IIC in January 2015. The IIC is a network for sharing advanced technologies and experiences aimed at promoting the development of the "Industrial Internet."
Siemens' Role in Industry 4.0 and the IIC
- Siemens is actively involved in all projects that promote business success, considering both technical and geographical aspects.
- As an international company, Siemens is also engaged in initiatives of Industry 4.0, playing a leading role in newly created platforms.
- Various approaches implemented within the initiatives help accelerate the process of global integration and standardization.
The Global Context of Industry 4.0
The digitalization of industry is a global topic. Discussions about digitalization are taking place worldwide, as the challenges faced by different countries prove to be similar.
- The need for the rapid market introduction of new products.
- Increasing product individualization in rapidly changing markets requires flexibility.
- The constant pursuit of efficiency improvement necessitates shortening development times and optimizing resources.
There are international initiatives aimed at accelerating the path to future manufacturing, such as Industry 4.0 in Germany and IIC in the USA. While the initiatives are similar, each country has its own peculiarities.
Governments around the world are investing in strengthening their manufacturing sectors. The main technologies of Industry 4.0 that require development include:
- In Germany, the main challenges are addressed by the government and associations that actively support initiatives in automation and protection of intellectual data.
- In the USA, leading roles are played by consortiums, such as IIC, which includes 170 companies from 30 countries, including German companies Bosch, Siemens, and SAP.
Furthermore, there are initiatives to support industrial innovations. For example, a national network for manufacturing innovation (NNMI) is being developed in the USA to facilitate collaboration between industry, science, and government.
Siemens' Example in Implementing Industry 4.0
The Amberg plant is considered an important example of Industry 4.0 implementation. Here are some key points about this plant:
- Production has increased 8 times since its opening in 1989, while the number of employees remains stable (around 1200 people).
- The production quality level has reached 99.9988%, minimizing the probability of failures.
- The use of Simatic control technology for over 1000 product variants.
- The plant produces about 15 million units of products per year.
- From the initial stages of production to delivery, approximately one thousand Simatic controllers are maintained.
