Automatic Circuit Breakers: Characteristics and Principle of Operation
Every automatic circuit breaker has a set of descriptions and distinct properties that reflect its functional capabilities. Breakers are classified according to technical and operational characteristics. In our company’s range, you will find devices of any power, as automatic circuit breakers are in particularly high demand.
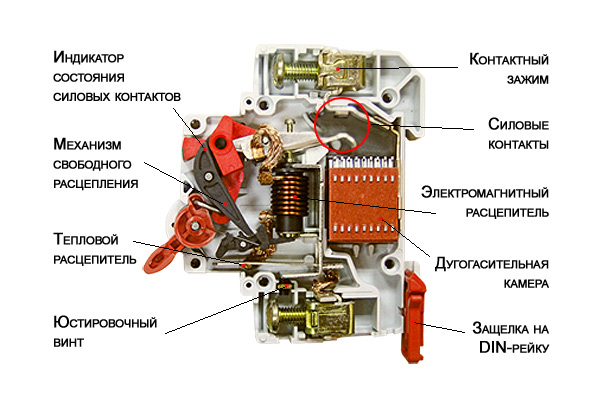
Operational Characteristics
Automatic circuit breakers have a number of operational characteristics:
- Mounting options for breakers;
- Degree of protection provided by the housing;
- Methods for connecting conductors;
- Placement categories;
- Climatic execution.
There are three options for connecting conductors:
- Wires or cables ending with cable lugs;
- Conductors with stripped insulation;
- Connection of electrical copper busbars with fork or pin connection.
Connections can be rear or front, with front being more convenient in operation.
Technical Specifications
Based on technical features, we can identify the following specifications:
- Instantaneous tripping current;
- PSC - maximum switching capacity;
- Rated current;
- Time characteristics;
- selectivity or application category;
- Overall dimensions;
- Number of poles.
An automatic circuit breaker is characterized by a current that causes the instantaneous tripping of the main contact pair. For modular and power breakers, different instantaneous protection values are established:
- In power breakers – the current value, multiple of the rated current or indicated in amperes;
- In modular ones, according to GOST R 50345-99, the protective characteristics are established: A, B, C, D, Z, K.
PSC is the value at which the breaker can separate the contact pair and subsequently allow the rated current to flow for a prolonged period. If PSC is exceeded, the breaker fails, which may lead to welding of the contact pair if the mechanical force stored in the breaker is insufficient.
The rated current refers to the current that allows the breaker to operate continuously without activating the protective trip. There are varieties of rated current:
- Of the automatic breaker, where conducting elements are taken into account;
- Of the thermal relay, which does not cause tripping, but adjusts the tripping device.
To choose an automatic circuit breaker, one should know the rated current in the network, which is calculated based on the power consumed.
The time characteristic of the breaker reflects the sensitivity of the breaker to trip operation, that is, the time required for the current that slightly exceeds the nominal to flow before the trip operation occurs. The type of time characteristic is denoted by a Latin letter.
Selectivity is classified into two types:
- A – breakers without selectivity;
- B – breakers designed to provide selectivity.
To ensure that the switching device occupies the necessary space during installation, it is essential to know its overall dimensions in advance. Breakers are produced with one, two, three, and four poles. The most relevant pole count for modular breakers is two poles. Our specialists will help you choose the best option. You can write to us, and we will get in touch with you.